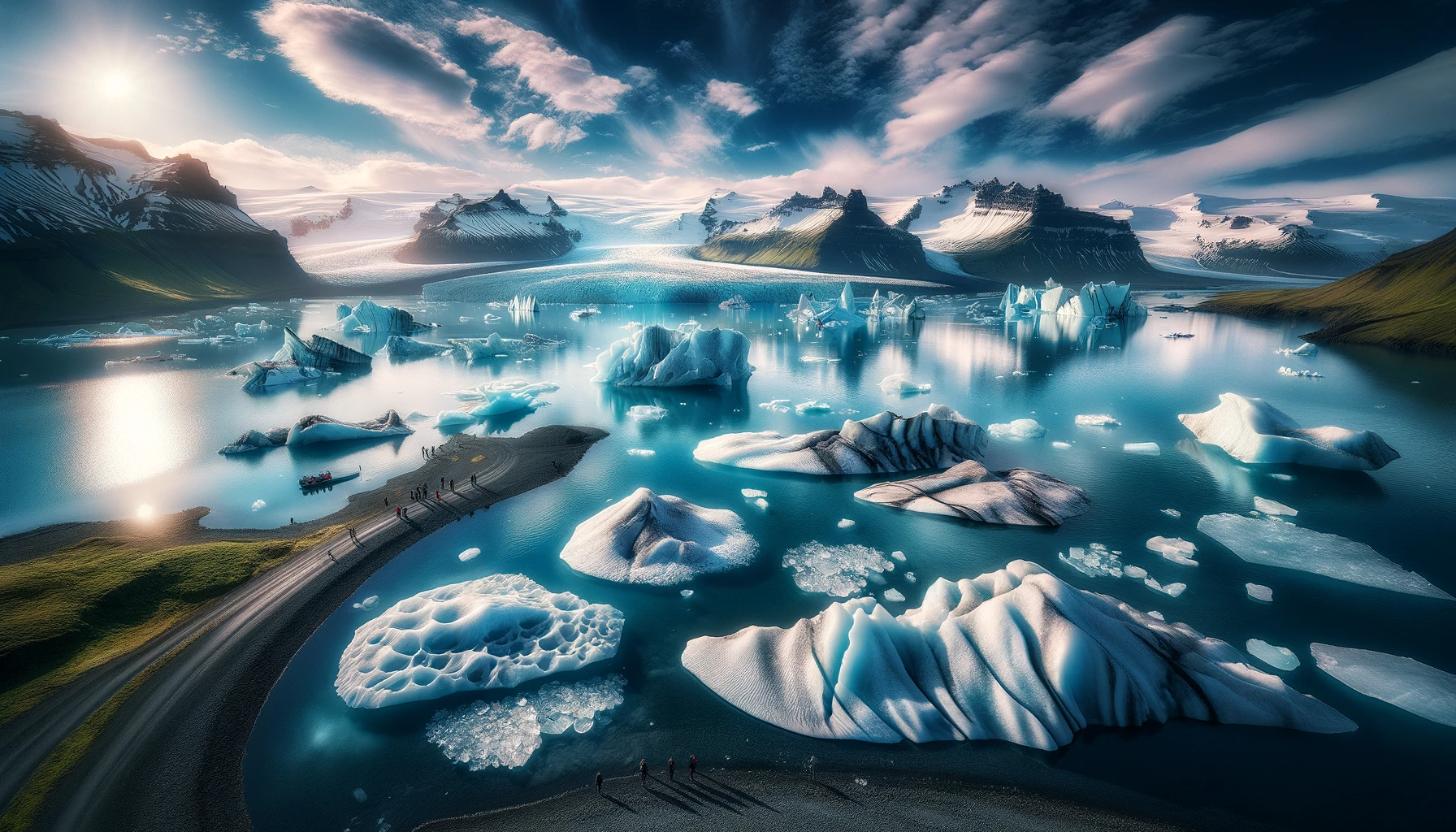
Iceland, a Nordic island nation, is renowned for its dramatic landscape with volcanoes, geysers, hot springs, and lava fields. Massive glaciers are protected in Vatnajökull and Snæfellsjökull national parks. Its capital, Reykjavik, runs on geothermal power and is home to the National and Saga museums, tracing Iceland’s Viking history. The country is known for its unique landscapes, northern lights, and rich Norse mythology, making it a fascinating destination for nature lovers and adventurers.
Public Holidays and National Holidays in Iceland for the year 2024
- New Year’s Day – Monday, 1 January 2024
- Maundy Thursday – Thursday, 28 March 2024
- Good Friday – Friday, 29 March 2024
- Easter Monday – Monday, 1 April 2024
- First Day of Summer – Thursday, 25 April 2024
- Labour Day – Wednesday, 1 May 2024
- Ascension Day – Thursday, 9 May 2024
- Whit Sunday – Sunday, 19 May 2024
- Whit Monday – Monday, 20 May 2024
- Independence Day – Monday, 17 June 2024
- Commerce Day – Monday, 5 August 2024
- Christmas Eve – Tuesday, 24 December 2024
- Christmas Day – Wednesday, 25 December 2024
- Boxing Day – Thursday, 26 December 2024
- New Year’s Eve – Tuesday, 31 December 2024
Iceland: A Land of Fire, Ice, and Natural Wonders
Introduction
Iceland, a Nordic island nation, is renowned for its dramatic landscapes of volcanoes, geysers, hot springs, and lava fields. This country combines natural beauty with a rich cultural heritage, making it a unique destination.
Historical Tapestry
Settled by Norsemen in the 9th century, Iceland’s history is steeped in Viking lore and sagas. Its parliamentary institution, the Althing, was established in 930 AD, making it one of the oldest in the world. Iceland gained independence from Denmark in 1944.
Geographical Marvels
Iceland’s geography is a study in contrasts, for example, the country features glaciers, such as Vatnajökull, and active volcanoes like Eyjafjallajökull. The rugged landscape is interspersed with black sand beaches, steep cliffs, and vibrant green valleys.

Cultural Richness
Icelandic culture is deeply connected to its Norse roots. The Icelandic language remains close to Old Norse. Traditional arts, literature, and music are integral to Icelandic identity. Modern Reykjavik is a hub of contemporary culture and creativity.
Economic Landscape
Traditionally dependent on fishing, Iceland’s economy has diversified. It now includes strong sectors in tourism, renewable energy, and technology. However, the country faces challenges like economic fluctuations and reliance on natural resources.
Political Framework
Iceland is a parliamentary republic. It has a president as head of state and a prime minister as head of government. Known for its progressive policies, Iceland is a leader in gender equality and environmental sustainability.
Society and Demographics
Iceland’s population is small but highly urbanized, with a strong focus on community, education, and egalitarianism. The nation ranks high in measures of quality of life, health care, and education.
Arts and Literature
Icelandic literature is famous worldwide, with medieval sagas that have influenced many contemporary writers. The country has a vibrant arts scene, with numerous festivals celebrating music, art, and literature.
Natural Phenomena and Tourism
Tourism plays a vital role in Iceland’s economy. Attractions include the Northern Lights, the Blue Lagoon, and the Golden Circle. The country is a prime destination for those seeking adventure and a connection with nature.
Global Engagement
Iceland is an active participant in international affairs. It is a member of the United Nations, NATO, and the European Economic Area. The country often mediates in global discussions on human rights and environmental issues.
Challenges and Prospects
Iceland faces challenges such as climate change impact and sustainable tourism management. Yet, it continues to innovate in areas like renewable energy and environmental protection.
Conclusion
Iceland offers a remarkable blend of natural splendor and cultural richness. Its commitment to sustainability, equality, and innovation makes it a model for future development. Iceland continues to inspire with its breathtaking landscapes and resilient spirit.







