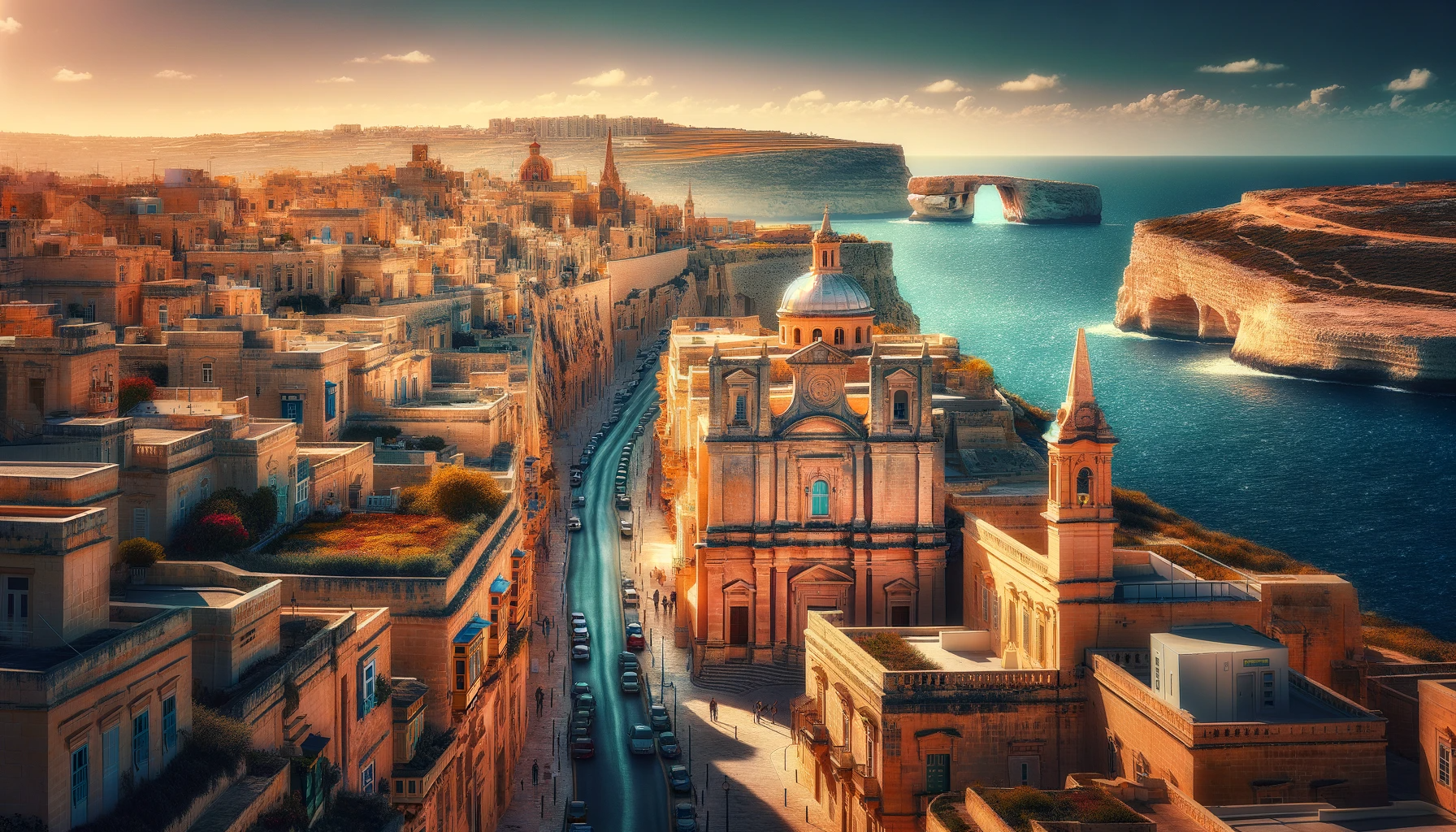
Malta is a country with a captivating history, rich cultural blend, and dynamic economy. Despite its small size, it plays a significant role in the Mediterranean region and continues to develop as a modern European nation.
List of Public Holidays in Malta for the year 2024
- New Year’s Day – Monday, 1 January 2024
- Feast of St Paul’s Shipwreck – Saturday, 10 February 2024
- Feast of St Joseph – Tuesday, 19 March 2024
- Good Friday – Friday, 29 March 2024
- Freedom Day – Sunday, 31 March 2024
- Workers’ Day – Wednesday, 1 May 2024
- Sette Giugno – Friday, 7 June 2024
- Feast of St Peter and St Paul – Saturday, 29 June 2024
- Feast of the Assumption – Thursday, 15 August 2024
- Victory Day – Sunday, 8 September 2024
- Independence Day – Saturday, 21 September 2024
- Immaculate Conception – Sunday, 8 December 2024
- Republic Day – Friday, 13 December 2024
- Christmas Day – Wednesday, 25 December 2024
History
- Ancient History: Malta’s history dates back to around 5200 BC, marked by ancient temples and archaeological sites.
- Strategic Importance: Due to its strategic location in the Mediterranean, Malta was ruled by various powers, including the Phoenicians, Romans, Moors, Knights of Saint John, French, and British.
- World War II and Independence: Played a significant role during World War II. Gained independence from Britain in 1964 and became a republic in 1974.
Geography
- Archipelago: An archipelago in the central Mediterranean between Sicily and the North African coast, consisting of three inhabited islands: Malta, Gozo, and Comino.
- Terrain and Climate: Characterized by a series of hills with terraced fields on the slopes, with a typically Mediterranean climate – mild winters and hot, dry summers.
Culture
- Rich Cultural Heritage: Influenced by various civilizations that occupied Malta over centuries, creating a unique blend of customs, traditions, and cuisine.
- Language: Maltese and English are official languages. Maltese is a Semitic language with Italian and English influences.
- Religion: Predominantly Roman Catholic, with impressive churches and religious festivals playing a significant part in Maltese culture.
Economy
- Diversified Economy: Traditionally based on industries like shipbuilding and textiles, but now diversified into tourism, finance, and iGaming.
- Tourism: A key sector, attracted by historical sites, vibrant nightlife, and beautiful beaches.
- EU Membership: Since joining the European Union in 2004, Malta has adopted the euro and integrated itself into the European economy.
Society
- Demographics: One of the most densely populated countries in the world, with a mix of Maltese and a growing expatriate community.
- Education and Healthcare: High standards of education and healthcare, often following the British model.
- Urbanization: Predominantly urban population with major towns including the capital city, Valletta, and the larger conurbations of Sliema and St. Julian’s.
Environmental Focus
- Challenges: Limited natural resources and issues like water scarcity, waste management, and conservation of its coastal and marine areas.
- Initiatives: Efforts in sustainable tourism, renewable energy, and protecting its rich marine life and bird species.
Government and Politics
- Political System: A parliamentary republic with a president as the head of state and a prime minister as the head of government.
- Legal System: Based on civil law traditions, with influences from Roman, continental, and British law.
Tourism
- Heritage and Attractions: Known for its historic sites related to its succession of rulers, including the Megalithic Temples, Valletta (a UNESCO World Heritage Site), and the medieval city of Mdina.
- Cultural Festivities: Hosts numerous festivals and events, showcasing its rich cultural tapestry, music, and arts.
Challenges and Future Outlook
- Economic Growth: Balancing economic growth with environmental and resource sustainability.
- Social Development: Addressing challenges related to urbanization, aging population, and integration of immigrants.
- Cultural Preservation: Efforts to preserve and promote its unique cultural heritage and language.

